Reciprocating compressors are described along with different parts, types, applications, advantages, disadvantages etc. Let’s explore Reciprocating compressors!
Reciprocating Compressors Basics
Let’s try to understand the basics of reciprocating compressors! There are some innovations and phenomena which hold massive value. We can also deduce that some natural attributes should be contained to get the maximum out of them. Whether it is related to channelizing the force or using fuel for combustion, everything is correlated.
- Compressors are also one of the pieces of equipment that is specifically used to increase gas pressure while containing its volume to the lower level.
- Here we will provide comprehensive information about one of the efficient types of compressors, i.e., known as a reciprocating compressor.
- Reciprocating compressors or piston compressors are the compressors in which the process takes place when the gas reaches the suction manifold.
- The gas then flows to the compressor’s subsequent part, which is known as a compression cylinder.
- This is the place where the gas is compressed with the help of a piston.
The reciprocating compressors are widely used in,
- Oil refineries
- Natural gas processing
- Refrigeration system
- Chemical plants
- HVAC system
- Instrument air skids etc.
This is the basic definition of the reciprocating compressor. Here we will provide all the information from top to bottom about the reciprocating compressor. Let’s start with the core definition or what is a reciprocating compressor all about?
What is a Reciprocating Compressor?
Reciprocating compressors are the compressors that use pistons that are attached inside the cylinder. It is a widely used compressor in various industries.
- A movable piston is present in each cylinder with a closed-end and resides next to the cylinder head.
- The piston is available at the other end.
- The movable piston is among the significant parts that play an essential role in compressing gases.
Lets try to understand the two cycles,
- In reciprocating compressors, the first stage of the compression constitutes air movement inside the cylinder through a suction valve.
- This is triggered by the piston movement, which helps in creating a vacuum.
- In the second cycle, the piston reverses the motion, which justifies this mechanical machinery’s name as the compression of air takes place.
- When the cylinder’s interior pressure increases, the pressure in the discharge pipe then valves open and effectively allows the cylinder’s air.
Apart from the above, the reciprocating compressor can also be defined as the machine in which the crankshaft is driven in a reciprocating motion. The intake gas that comes out from the crankshaft can then be used for different purposes. Mainly these are used for industrial purposes.
Parts of Reciprocating Compressors
The components of a reciprocating compressor can easily be elaborated based on specific groups. Mainly there are four groups in which every part complies. The following are the brief description of them:
Outer shell
This is the base in which different parts of the compressor are attached. It is mainly composed of,
- the body,
- the crankcase, and
- the middle body.
Transmission Mechanism
The whole movement of the components while getting towards the compression mechanism holds different parts such as,
- a clutch,
- a belt wheel or coupling,
- another driving device,
- a crankshaft,
- a connecting rod,
- a crosshead,
- and few other moving parts.
With these parts reciprocating linear motion is achieved by converting rotary motion.
Compression Mechanism
Compression is the core mechanism that includes different parts of the compressors. The whole mechanism consists of different parts such as,
- cylinder,
- piston assembly,
- air inlet,
- exhaust valve, etc.
Subsidiary Bodies
These are the different parts of compressor design that hold their importance. This group of components constitutes,
- cooler,
- buffer,
- oil-water separator,
- various pipelines,
- circulating oil system,
- cooling water system,
- turning gear,
- valves,
- electrical equipment,
- protective
- covering device,
- safety cover,
- net, etc.
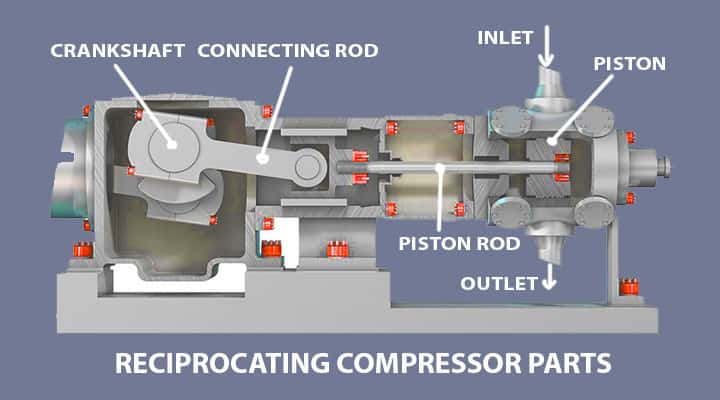
While understanding the mechanism, it is quite significant to get an idea about the reciprocating compressor’s different parts. These parts will helps us explicitly to understand the whole process of compression. The following are the important parts of the reciprocating compressors:
Compression Cylinders
The compression cylinders are the core part of a reciprocating compressor. These are also known as stages.
- The design of this compressor may vary as the arrangement can insert 1-6 cylinders.
- These are mainly to confine the process of gas compression.
- Then a piston is arranged that compresses the gas.
As per the design, it can be single or double-acting. In the dual-acting design, the compression takes place on both sides of the piston.
Unloaders and Clearance Pockets
These are special valves that regulate the percent of load carried by the compressor when equipped with the driver’s rotational speed. Unloaders are used for calibration that controls the suction valves, ultimately allowing the gas to recycle. The clearance pocket valve changes the cylinder headspace. These are present in the compressor, either fixed or variable volume. An overview of this component will happen to understand the core functioning.
Doghouse
The doghouse is a structural part that connects the cylinder and the compressor frame. Here it is quite significant to keep a check on the intermixing of fluids between the cylinder and doghouse must be restrained.
- The doghouse help invent the most dangerous part of the compression, i.e., the compressed gas.
- In addition to that, it is also equipped with packing rings that are designed to contain the gas in the cylinder.
Running Gear
Running gear is the compressor that is attached to the frame and contains a crosshead and connecting rod.
- This part connects the piston rod to the crankshaft.
- This helps in attaining the reciprocating linear motion from the rotary motion.
Crankshaft
The crankshafts are the parts that hold or effectively balance the dynamic forces. These dynamic forces are the product of the movements of the heavy pistons.
- The plain bearings effectively support it at different points.
- In addition to that, it has a flywheel that helps in storing the rotational inertia.
- With that, it also provides a mechanical advantage for manual rotation.
Lubrication System
One of the major parts that keeps a specific place is the lubrication system. Most of the compressors need proper running gear that is lubricated to get practical and extensive motion. This system doesn’t only hold the lubrication but also consists of,
- lubricant temperature control,
- numerous instrumentation and redundancy measures, and
- filtration.
Suction Strainers and Separators
The role of suction in reciprocating compressors is vital as all the gases effectively pass through separators and suction strainers.
- These parts help in removing the entrained particles, moisture, and other phase process fluid.
- Suction strainers and separators are quite significant, and the ill-functioning of any of them causes massive damage.
- It may even threaten the integrity of the cylinder, which can cause a massive hazard.
Pulsation dampeners
These are the practical parts that help in providing a capacitance that makes the flow and pressures appropriate. This is dependent on the compression stroke.
Electric motor
The reciprocating compressors generally are low-speed machinery which can be easily driven by a belt or direct electric motor.
- These are calibrated with or without variable speed drive controllers.
- When it comes to those parts that hold massive value, the electric motor keeps the topmost position.
- Apart from this, there are different steam turbines or other sources of power such as diesel engines or natural gas engines.
Mechanism of Reciprocating Compressor
Reciprocating Compressor Working Basics
Let’s try to understand the basic thermodynamic cycles of reciprocating compressors. Compressors, as the name suggests, incurs compression. This compression happens in the cylinder. There are total four cycles,
- compression,
- discharge,
- expansion and
- intake.
In this thermodynamic cycle, each cycle has two strokes. See below P-V Diagram for the graphical representations.
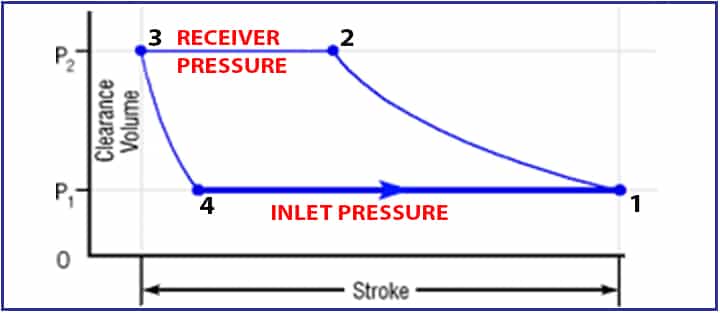
- P1: Pressure at suction side at point 1
- T1: Temperature at suction side at point 1
- V1: Volume at point 1
In the initial stage, the piston is at point1, and the volume, pressure, and temperature is V1, P1 & T1 respectively and suction and discharge valves are closed at that time. Now piston advances towards opposites (that is from top dead center to bottom dead center) and it compresses the air or gas inside the cylinder.
- Volume reduces
- Pressure & temperature increases
- Pressure becomes equal to the discharge pressure and discharge valve opens at point 2
- Pressure at point 2 becomes P2 and discharge it to a receiver.
There is a clearance volume to avert piston/head contact which increase the life of compressors. Point 3 is indicated for that. After this process, expansion happens a little lower to the suction pressure. This time discharge valve is closed at point 4. The same cycle continues.
How Does Reciprocating Compressor Works?
The core mechanism of a reciprocating compressor is not that complex. We can understand it through stepwise methods:
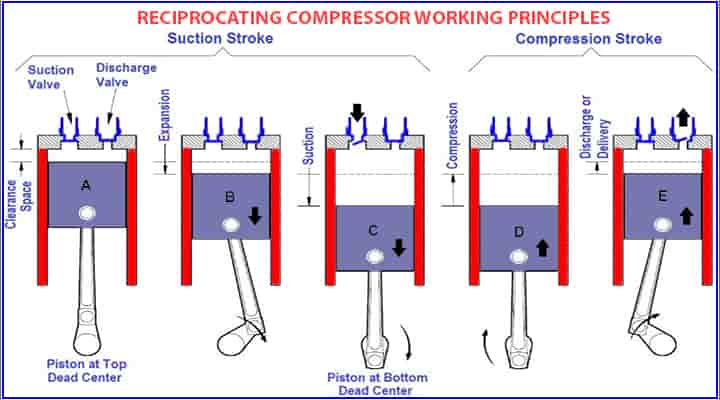
- The first step complies in which process gas is drawn into the cylinder. It is then compressed and released through a mechanical valve.
- These mechanical valves operate automatically by the change in pressure. The whole system has a different design which consists of different numbers of suction and discharge valves.
- The crankshaft comes into function after the first step as it is fitted with counterweights that balances the ever-changing forces produced by the movement of the heavy pistons present in the cylinder.
- The function of suction strainers comes into play as the suction gases pass through these.
These are relatively low-speed devices and run-on electric motors, which a variable speed drive controller calibrates.
Types of Reciprocating Compressors
Reciprocating compressors are classified based on the two scenarios,
- Based on numbers of discharge stroke per revolution
- Based on the speed or drive mechanism
There are two kinds of the same available on the basic use of pistons when it comes to discharge stroke per revolution. A brief discussion about the same are as follows:
Single-Acting Reciprocating Compressor
This is one of the most common types of reciprocating compressors available in the market.
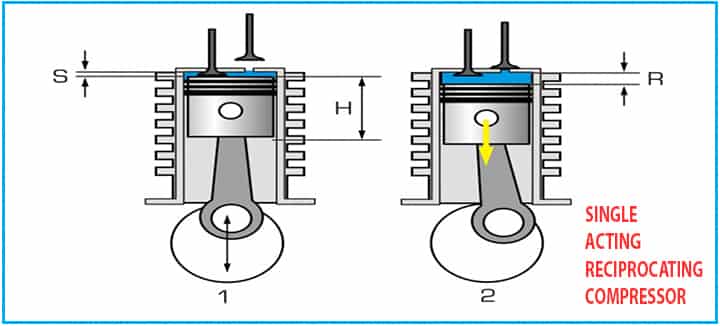
- These are quite powerful when it comes to weight and size.
- However, these are quite loud.
- The simple design of this reciprocating compressor holds the crux of the same.
- It provides maximum portability, and it can be attached to the point without considering many installations of piping and connections.
- The maintenance cost of this type of reciprocating compressor is relatively low.
Single-acting compressors are pretty effective, but as compared to their counterparts, these are quite expensive. These are specifically used in those places where constant pressure is not required.
Double-Acting Reciprocating Compressor
This reciprocating compressor is given because it uses both sides of the piston to compress the air.
- It helps in providing efficient compression as compared to the single-acting one.
- Double-acting compressors are widely used for industrial purposes.
- One of the main benefits of this compressor is its simplistic maintenance approach.
- However, it needs huge space, and the cost associated with this is also high.
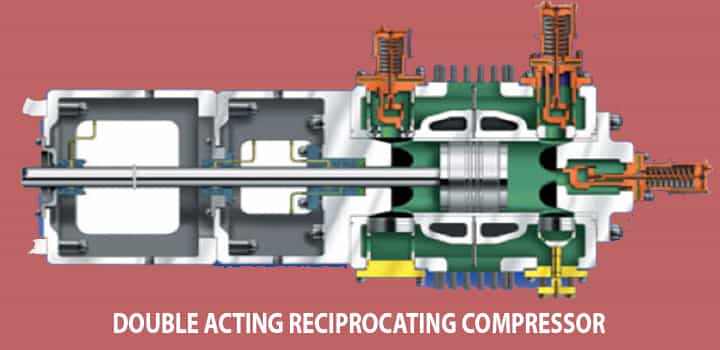
The vibration generation due to its operation is quite annoying as it needs special mountings that keep it in one place. Now based on speed or drive mechanism, reciprocating compressors are classified into two categories,
High Speed or Separable
- Separable reciprocating compressor, as the name suggests, the driver is separated from the main compressor. Motor or engines are used as drivers.
- Very high speed.
- Efficiency is low.
- Low initial cost and low operational cost.
Low Speed or Integral
- Integral reciprocating compressor, as the name suggests, the driver is integral with the main compressor.
- Low speed.
- Efficiency is high.
- High initial cost and low operational cost,
Applications of Reciprocating Compressors
The applications of these compressors are quite wide. It is used for different purposes in almost every sector. Here we are providing some of the core application sectors of these compressors:
Oil refinery: The use of reciprocating compressors in oil refineries is evident. It is among the most popular sectors that use these compressors. However, almost all the popular industries need it. In the oil refineries, crude oil is processed, and there are numerous processes attached to this through which useful products such as,
- diesel fuel,
- gasoline,
- heating oil,
- kerosene,
- liquefied petroleum gas and
- asphalt bases are produced.
These are produced with the help of a compressor and carry the fluid from one chemical processing unit to another.
Pipeline transport: The movement of fluid and using these reciprocating compressors in the pipeline is quite popular.
- The basis of reciprocating compressor is needed when we need to transport different materials in the pipes.
- With this process, we can quickly transfer gases and liquids.
Nowadays, we are also using pneumatic tubes that are capable of transporting solid also.
Chemical plants: Another prominent sector that uses reciprocating compressors is a chemical plant. Those plants which process any chemical on a large scale always used reciprocating compressors.
- Through the operation of compressors, different biological and chemical transformations take place.
- Most of the time, the operation of a reciprocating compressor is the same as in refineries.
Perks and Limitations of Reciprocating Compressors
Perks: There are several benefits of reciprocating compressors. Some of them are compiled as follows:
- These are specifically used to produce high-pressure gas.
- The reciprocating compressors are capable of compressing refrigerants and gases.
- It provides maximum efficiency and flexibility.
- These reciprocating compressors come in cheap and rugged designs.
Drawbacks: The drawbacks of reciprocating compressors are pretty abundant, and the following are some of them:
- The absence of self-regulation is among the foremost backdrops of the compressors.
- It continues to displace the gas until directed not to
- The major backdrop of compressors is their massive sizes.
- The frictional resistance between the cylinder and piston causes the loss of work input.
- The whole process is quite rugged, and the possibility of pulsation of fluid flow persists readily.
- While in operation, it causes high vibration and noise.
- The essential parts, i.e., piston valves and rings, are sensitive to the fluid’s dirt.
Parameters to Select Reciprocating Compressor
While selecting an adequate compressor, one should keep a check on some effective parameters. These parameters are pretty critical and should be considered at any cost.
Components: The components of compressors are the significant aspect that helps in selecting an appropriate one.
- When you are selecting a reciprocating air compressor, you need to keep a keen check on pistons.
- However, other components are also quite efficient, such as Valves, connecting rods, and crankshafts.
Maintenance: While selecting these compressors, one should keep a check on quality components as it reduces the While maintenance costs. While choosing a compressor, look for less expensive parts and a simplistic design.
Pressure: Pressure is one of the most important factors that has practical advantages. After all, a compressor’s primary purpose is to formulate the pressure and compress the gas or liquid.
- Reciprocating compressors are those which are capable of providing sufficient pressure as compared to other kinds.
- However, other types of compressors, such as centrifugal, are more efficient than reciprocating compressors.
Cost: When it comes to selecting the compressor, the buyer should keep a check on cost. The initial cost associated with the compressor is a prominent factor.
- As compared to other kinds of compressors, the reciprocating compressor comes under a low budget and provides maximum efficiency.
- However, the service life of reciprocating compressors is comparatively lesser to others.
- The reciprocating compressors are equipped with numerous parts that need optimal maintenance.
- While selecting one, keep a check on this factor.
Heat Dissipation: The heat dissipation by the compressor is a prominent factor. While operating the compressor, heat dissipation affects the durability as well as longevity of the machinery.
- In reciprocating compressors, the internal friction due to the piston movement and cylinder functionality causes massive heat production.
- If you choose a reciprocating compressor, then be ready for increased maintenance cost as the hotter environment takes a toll on the delicate components.
Noise: Some compressors produce heavy vibrations and noise. Where there is a need for continuous communication, the compressor with low noise is preferred.
- Reciprocating compressors produce high amounts of noise that restrain adequate working conditions.
- However, there are other compressors also which have low noise.
- One of the best types of compressors on the front of noise and efficiency, the single-acting reciprocating compressor is an apt choice.
Reciprocating compressors are different from rotary compressors. Do you want to know the differences between them?
Difference between Reciprocating Compressor & Rotary Compressor
Let’s see the basic differences between reciprocating compressors and rotary compressors:
| Reciprocating Compressors | Rotary Compressors |
| Reciprocating compressor has piston arrangement and works based on the reciprocating motion of piston. | Rotary compressor has no piston arrangement and works based on the rolling action. |
| To generate very high delivery pressure (1000 bar), this types of compressors are used. | To generate low delivery pressure (10 bar), this types of compressors are used. |
| Pressure ratio is high. | Pressure ratio is low. |
| Main application is low volume flow rate with high pressure. | Main application is large volume flow rate with low pressure. |
| Complex design & high space requirement. | Simple design & low space requirement. |
| Free air delivery is less comparative (300 m3/min) to rotary compressor | Free air delivery is high comparative (3000 m3/min) to reciprocating compressor |
| It operates at low rotational speed. | It operates at very high rotational speed. |
| Due to presence of unbalanced forces, this compressor is difficult to balance. | No balancing problems |
| Lubrication process is complex and air comes in contact with lubrication oil. | Lubrication process is simple and air doesn’t come in contact with lubrication oil. |
| Noise & vibration is high | Noise & vibration is less |
| Efficiency is high, as compression ratio is high. | Efficiency is low comparative to reciprocating compressor, as compression ratio is low. |
| Initial cost is high. | Initial cost is low. |
| High maintenance due to many rotating parts | Low maintenance due to lower numbers of rotating parts |
| Air is internment due to reciprocating action. | Air is continuous due to rotary action. |
| Works based on complete Brayton cycle. | It works only in one step of Rankine cycle. |
Codes and Standards for Reciprocating Compressors
There are a few design codes and standards available for the design of reciprocating compressors, as follows:
- API-11P – Packaged Reciprocating Compressors
- API-618 – Reciprocating Compressors
- IS 11461: Code of practice for compressor safety
Manufacturers of Reciprocating Compressors
There are so many manufacturers available for reciprocating compressors, few of them are listed,
- Milton Roy
- Neumann & Esser
- GEC
- Ingersoll Rand
- LEWA
- BAC compressors
- Kaeser
- Atlas Copco
- Kulmec etc.
Conclusion
With the holistic knowledge of reciprocating compressors, it is pretty easy to select the effective one. This article holds all the information, such as the core definition and the definition of its type. With this, you can get an overview of one of the efficient kinds of compressors. In addition to all the information, the credible benefits will help you to get the perspective clear. We have also provided some of the parameters that are pretty effective for selecting an appropriate compressor as per the need.

it is usefull