Let’s learn steam boiler along with basics, definition, parts, working principle, types, advantages, disadvantages, applications. Let’s explore steam boiler!
What is Steam Boiler? Definition
Steam Boiler Basics
Let’s explore the basics of a boiler or a steam boiler. What do you mean by steam boiler? As the name suggests, it is clearly understood that it is an equipment which is used to boil water to form steam. Normally, steam is produced, so it is called a steam boiler! For example, to understand the basics, take a closed container or a closed vessel with some water. Now, if you boil it, what will happen?
- Water will be heated
- Steam will be formed
- Gradual increase in pressure
- Safety valve will be opened

Hence, it is understood that if we boil water, high-pressure steam will be produced. Now, this steam is used in many industrial plants like thermal power plants, nuclear power plants, etc. to produce power. Hence, steam boiler is an essential part of many industries.
Steam Boiler Definition
A steam boiler is a power generation device that generates steam by applying heat energy to water. It is in the form of a closed vessel made up of steel in which combustion of fuel occurs to produce heat energy. It is also called a steam generator.
A steam boiler is a critical part of a thermal powerplant, therefore, it’s important for us to have knowledge about the steam boiler.
History of Steam Boilers
The invention of the steam boiler has been started at the end of the 1700s with a simple kettle type boiler.
- It was used to produce steam other than any industrial applications.
- There was a fire box to produce heat and one water kettle was kept on the box.
- Due to the heat from fire box, water was heated & produced steam.
- It was very small and fired by hand only.
- Small heat output as well as small steam output.
In 1967, the boiler was further developed for industries. Mainly G. Babcock and S. Wilcox were founded steam-generating industrial boilers. In 1679, Denis Papin further developed the steam boiler with a safety valve and started to use it in many industries.
In 1891, Stirling Boiler Company started to make boilers and boost the various industry with the application of steam boilers. In 1907, Stirling Boiler Company and Babcock & Wilcox Company are joined and started to make the best quality, customized, various capacity boilers.
Main Parts of Steam Boiler
A steam boiler is a complex combination of,
- Shell,
- Furnace,
- Boiler mountings,
- Accessories,
- Heating space,
- Grate,
- Water space, and
- Steam space.
Let’s try to understand each of the parts of the boiler to have a basic idea.
- Shell: The boiler shell is a hollow cylindrical body made of steel. The heat transfer and steam generation will occur in this part. The ends of the shell are closed with endplates.
- Furnace: Here the combustion of fuel occurs to produce heat energy. The burner creates combustion in this chamber by burning various types of fuel. It lies over the grate and below the shell.
- Boiler Mountings: These are the fittings and devices for proper functioning and safety of the boiler (pressure gauge, safety valve, stop valve, etc.)
- Accessories: These are the integral devices fitted on the boiler to improve its efficiency (superheater, air preheater, economizer, etc.)
- Grate: It is the space in which fuel is burnt. It is built of several cast-iron bars which are used to support fuel placed on it.
- Heating space: This space is exposed to hot gases on one side and water on the other.
- Water space and steam space: These two areas are part of the shell. Water space is the volume occupied by water in the shell and steam space is the area where steam got collected inside the shell of the boiler.
How Does a Steam Boiler Works?
It’s a very common question that how does a steam boiler work? Let’s try to understand in the simplest way,
Working Principle Basics
Water is readily available and it is the lowest cost, easily handled liquid. When we talk about thermal energy, water becomes the first choice. We don’t understand the energy contains in the water normally, but if you transform the water into steam, it can easily get an idea!
Take,
- Volume of water = V
- Now, if you make it steam, it volume will reach approximately, 1600 x V
It means huge energy can be generated from water.
Check a very nice ANIMATED VIDEO from Lesics,
Steam Boiler Working Process
Let’s see the working process of a steam boiler in step by step,
- Water feeding to the shell of the boiler at operating pressure.
- Fuel is burnt in a furnace and hot gases are produced.
- These hot gases come in contact with water space.
- The heat transfer occurs from hot gases to water in the shell.
- The water gets heated and converted into steam.
- The steam is collected in steam space for further use.
- This steam can be used for power production, air conditioning and to perform any industrial process.
Types of Steam Boiler
We can classify steam boilers into various types based on their uses/applications. Factors on which the boiler can be classified are;
- According to tube content
- Method of circulation
- Number of tubes
- Heat source
- Pressure
- Shell axis
- Location of furnace
- Mobility
According to tube content
The tube of the boiler will either contain water or flue gases. Therefore, there are two types of boiler on the basis of tube content.
- Water tube boiler
- Fire tube boiler
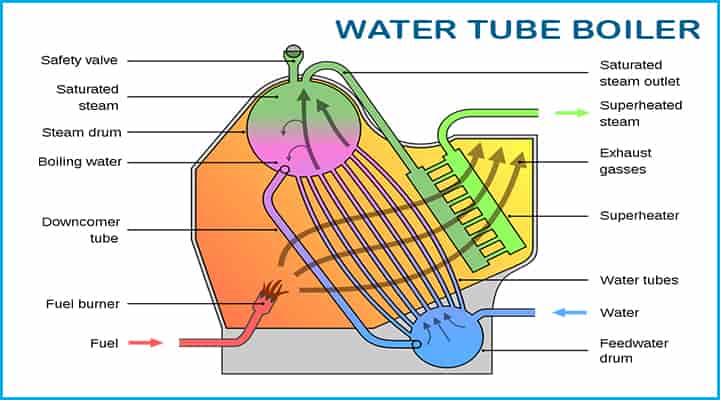
Water-tube boiler: As the name suggests, the tube consists of water, basically, a water tube boiler means, water is contained inside the tubes.
 via Wikimedia Commons
via Wikimedia Commons
- The tubes are surrounded by flames and flue gases from outside.
- Heat transfer occurs from flue gases to tubes filled with water through the walls of the tubes.
- They are useful in huge powerplants where the amount of steam demand and pressure are high.
- Steam can be easily generated by increasing surface area through a large number of tubes.
- They are very common and utilized for large power requirements.
- This type of boiler has a high rate of heat transfer resulting in higher efficiency.
- In the beginning, they are called non-explosive boilers as they solve the problem of a boiler explosion at that time.
- This type of boiler works in a pressure range of 12 to 100 bar and steam capacities from 0.63 to 63 kg/s.
- Water tube boiler has the advantage of safety, rapid heat transmission, and fast reaction to meet steam demand.
- On the other hand, it has a higher initial cost, is big in size, and more complicated to operate in comparison to the fire tube boiler.
- Examples of water tube boilers are Babcock and Wilcox boiler, Benson, Stirling boiler, etc.
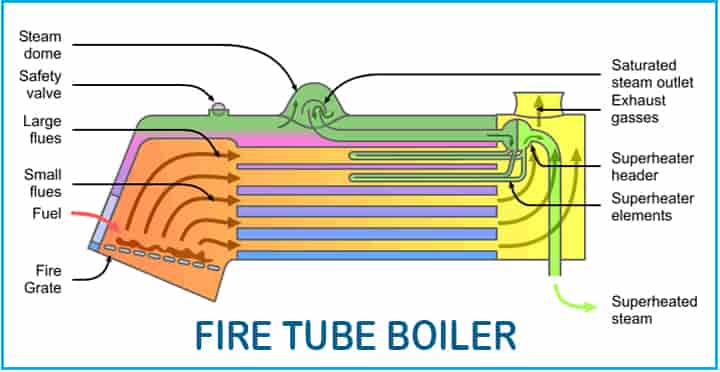
Fire-tube boiler: The Fire-tube boiler, as the name implies, the tube consists of fire. Basically, in fire tube boilers, fire is contained inside the tubes. They are also called smoke tube boilers.
 via Wikimedia Commons
via Wikimedia Commons
- The tubes are submerged into the water inside the shell.
- Heat is transferred from hot tubes to the surrounding water through the walls of the tubes.
- They are useful in small powerplants where the amount of steam demand and pressure are low.
- They are utilized for small power requirements.
- This type of boiler has lower efficiency.
- They have a problem with explosions as tubes contain hot gases at high temperatures and pressure.
- This type of boiler works up to maximum pressure of 17.5 bar and steam capacity up to 10 kg/sec.
- The fire tube boiler has the advantage of lower initial cost, compact design, and easier operation.
- On the other hand, they have a risk of explosion, large water volume resulting in poor circulation, as well as more time is required for steam to reach the desired pressure.
- Examples of fire tube boiler are Scotch marine, Cochran, Lancashire and locomotive boiler, etc.
According to Method of Circulation
We are dealing with two types of steam boilers based on the circulation of water. They are;
- Natural boiler
- Forced boiler
Natural boiler: Water is present in a vessel, if we heat it the density of the bottom portion is decreased in comparison to the density of the upper portion.
- Less dense water from the bottom will rise up to the top, this will continue till the temperature of all water becomes the same.
- This method of circulation of water is free circulation and this is applied in the natural boiler.
In a natural boiler, unequal expansion of parts of the boiler can be prevented as we have uniform temperature everywhere in the boiler. Also overheating of boiler plates can be minimized.
Examples;
- Babcock and Wilcox boiler

- Lancashire boiler
Forced boiler: In this type of boiler, pumps are used to maintain the continuous flow of water. The centrifugal pump creates the pressure for water circulation. Forced boilers are high-pressure and high capacity boilers.
- It has a higher rate of heat transfer; easy control of fluctuation load and steam generation is quick.
- We can reduce the size and weight of the boiler by using forced circulation of water.
According to the number of tubes used
Based on the number of tubes, we have two types of boilers;
Single tube boiler: As the name specifies, a single tube boiler contains only one fire tube or water tube. Cornish boiler is a single tube boiler.
Multi-tube boiler: This boiler has a number of tubes for flue gases or water. An example of a multi-tube boiler is the Cochran boiler.
According to the heat source used
We have the following types of boilers according to fuel used;
- Solid fuel-fired (Babcock and Wilcox boiler)
- Liquid fuel-fired (Volex boiler)
- Gas fuel-fired (Babcock and Wilcox boiler)
- Nuclear fired (used in nuclear power plants)
- Electrically fired (use of electrodes inside the shell of the boiler)
According to Pressure
There are three types of boilers on the basis of pressure.
- Low-pressure boiler: Work at a pressure range of 15-20 bar. It is used for process heating.
- Medium-pressure boiler: Work at a pressure range of 20 to 80 bar. It is used for power generation and process heating.
- High-pressure boiler: Work at a pressure above 80 bar. Loeffler boiler is a high-pressure boiler.
According to Shell Axis
On this basis, two types of steam boilers are;
- Horizontal boiler: The shell axis is horizontal here; an example is the Lancashire boiler.
- Vertical boiler: The shell axis is vertical here; an example is the Cochran boiler.
According to the location of the furnace
According to this factor, types of boilers are;
Internally fired boiler:
- The furnace is present inside the boiler shell.
- Many fire tube boilers are internally fired boilers.
- Examples are Stirling, Babcock, and Wilcox boiler.
Externally fired boiler:
- The furnace is located outside the boiler shell.
- In this boiler, the furnace is placed underneath the brickwork setting.
- Water tube boilers are always externally fired boiler.
- Examples are Cochran, Lancashire boiler.
According to Mobility
On the basis of mobility, boilers are following types;
- Stationary boiler
- Portable boiler
Stationary boiler: This type of boiler is stationary, used in industries (sugar, chemical, textile, etc.) for process work and generation of thermal power. Examples;
- Babcock and Wilcox boiler
- Lancashire
Portable boiler: This boiler can be moved from one to another. Examples are locomotive and marine boilers.
Advantages of Steam Boiler
- Steam is generated to be used for various useful purposes.
- We can run a turbine or engine when coupled with a steam boiler.
- Flexibility to design and operate boiler according to our needs.
- Any kind of chimney can be used.
- Construction costs can be easily minimized.
Disadvantages of Steam Boiler
- Running a steam boiler is a critical job.
- High temperature and pressure are involved.
- Occupies suitable floor area.
- A well-trained employee is required.
- The boiler needs to be regularly looked after.
- To prevent heat burns, most of the area of the boiler should be insulated.
- The boiler increases the temperature of a room and continuous stay in that room is not possible.
Applications of Steam Boiler
From the beginning, steam boilers were used in transportation to run trains and ships. Some of the recent applications are;
- Power Production (Operating steam engine, turbine, reciprocating engine)
- Air Conditioning
- Industrial Usage (Process work in chemical, textile, and sugar mills)
- Sterilization of surgical instruments
- Domestic water heating for cold areas
Desirable Properties of Steam Boiler
We need a boiler with the following properties;
- Capital and running costs should be less.
- The boiler should be more efficient.
- Occupies less space and is lightweight.
- Maximum steam generation with less fuel utilization.
- The boiler should be safe under high operating conditions.
- Various parts of the boiler should be easily accessible for repair and maintenance.
- Capable of quick starting and loading.
Factors of Steam Boiler Selection
To select a boiler among many, the following factors should be considered;
- Cost of boiler: Select a boiler that matches your budget.
- Space or floor area required: Make sure you have sufficient area to easily adjust the boiler.
- Water and fuel availability: Arrange a source of water and fuel for boiler operation.
- Capacity requirement: Compare your required capacity with catalogue capacity.
Steam Boiler Efficiency
It is the ratio of energy received by water to the energy supplied by the fuel for steam production.
Steam boiler efficiency = Energy gained by water/Total energy input = ṁs (h2-h1)/ṁ CV X 100
Where,
- ṁs = mass of steam generated in a given time
- ṁ = mass of fuel used in the same time
- h2 = Enthalpy of steam
- h1 = Enthalpy of feed water
- CV = Calorific value of fuel
Types of Fuels in Steam Boiler
Three types of fuel are used in the boiler which are;
- Solid fuel: This fuel is in solid form. It includes wood, coal, pet coke, and rice husks.
- Liquid fuel: This type of fuel is in liquid form. It includes furnace oil, light diesel oil.
- Gaseous fuel: This fuel is in gaseous form.
It includes,
- LPG (Liquified Petroleum Gas),
- LNG (Liquified Natural Gas), and
- PNG (Piped Natural Gas).
Conclusion
Complete details of the steam boiler and boiler types are specified. Hope it clarifies your concepts and helps you understand steam boiler working. If you have any queries regarding any part of this topic, feel free to contact us. We will love to answer. Also, if you want to add something please mention it by writing to us. Thanks.
