The Thermal power plant, as the name suggests, generates power from the thermal energy. This is the most conventional power plant all over the world. Each country, a huge amount of power is generated by the thermal power plant. In this session, we will learn the details of the thermal power plant, it’s working principle, various diagrams, advantages, disadvantages, examples to get a detailed overview.
What is Thermal power plant? Definition
What is a thermal power plant?
A thermal power plant uses thermal energy from fuel to produce electric power. Normally coal is used as the source of thermal energy.
- This thermal energy is used to heat water and produce steam.
- Steam is used to pass through the turbine
- Turbine rotates
- The rotation of the turbine helps to produce power at the generator.
Due to the use of coal in thermal power plant, it is known as a coal-based thermal power plant or coal thermal power plant. In addition to that, due to the use of steam, turbine arrangement, it is also known as a steam turbine power plant. So, what is the thermal power plant?
Thermal Power Plant Definition
A thermal power plant is one kind of plant or system, which is used to produce electrical power by using thermal energy.

- Coal is mainly used as fuel.
- Normally brown, bituminous, and peat coals are widely used.
- Water is used as secondary fuel which helps to transfer thermal energy from coal.
- There are various components of thermal power plants.
History
The thermal power plant is continuously developed since the 18th century. Initially, reciprocating engines were used to produce mechanical power by producing steam. In 1884, the steam turbine was introduced to increase efficiency, and finally, it was totally improved in 1905 by replacing an entire reciprocating system in the central power plant.
Why thermal power plants are required?
The thermal power plant is based on old methodologies. The demand for power is increasing day by day. It is a relatively cheap power cost comparative to nuclear power plants, solar power plants, or hydro-power plants, and it helps to meet the power demands. Although many countries are installing clean energy or renewable plants, thermal power plants are widely taking part to produce a huge amount of power for us.
- Coal is easily available
- Coal is cheap
- The cost of nuclear power plants, solar power plants are too high.
- Hydro-power plants are based on the water head availability.
- Installed renewable power plants are not able to meet the requirements.
- The huge amount of coal is available in many countries
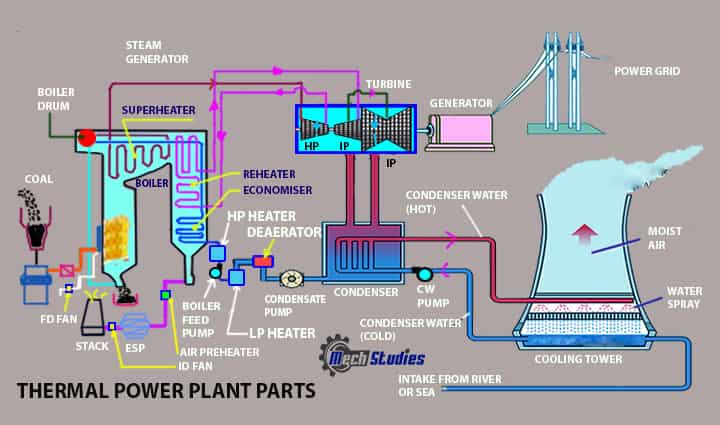
What are the Components of Thermal Power Plant? Parts
The main parts of Thermal Power Plant:
- Coal handling system
- Boiler feed pumps
- Boiler
- Turbine
- Condenser
- Condensate extraction pumps
- Circulating pumps
- Cooling tower
- Generator
- FD & ID fans
- ESP
- Chimney
- Ash handling system
- Water treatment plant
01. Coal Handling Plant
Fuel coal is crushed here by the crushing machine, and it is fed to the furnace of the boiler by conveyer belt.
02. Boiler
The boiler is the main component of a coal-based power plant. There are different kinds of boilers, like water tube boilers, fire tube boilers, etc. However, for example, purposes, we have considered a water tube boiler.
It consists,
- Furnace
- Water tubes
- Boiler drum (main drum)
- Water drum (mud drum)
- Economizer
- Superheater
- Evaporator
- Water preheater
Furnace & water tubes
The furnace is the main heat-generating equipment in the boiler. The combustion of fuel happens in the furnace.
- The Water-tube boiler consists of the furnace.
- Water flows through these tubes.
- Coal and air are burned in the furnace.
- The heat from the combustion heats the tube as well as the water inside the tube.
- Remember in the case of a fire tube boiler, the tube doesn’t have water, it has hot gases instead of water.
Boiler drum
A drum is provided in the boiler to collect steam. Here, hot water and steam is separated with the help of a steam separator.
- Separated steam is passing through the superheater.
- Separated water is going to the water drum.
- It stores the water.
- There is a continuous blowdown process to reduce the water TDS level.
- If the water level is crossed the highest level, emergency blowdown opts.
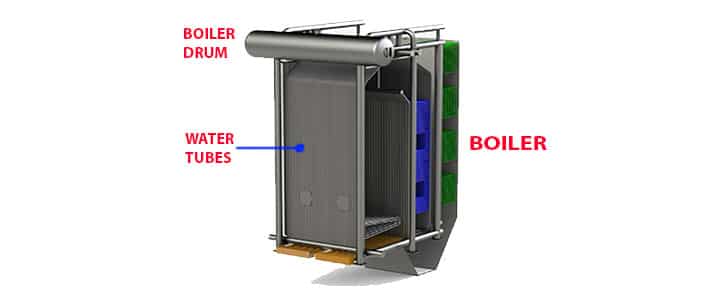
Mud or Water Drum
This water drum is connected to the main boiler drum, kept at the top of the boiler, through the water bundles.
- Solids or unwanted foreign particles are settled in the water drum.
- Based on the requirements, these settled particles are removed by blowdown.
Superheater
A superheater is a device used to convert saturated steam into superheated steam. Superheat means the temperature of the steam is further increased than the saturated steam.
- These are high-grade tubes
- Normally made of high-grade stainless steel or nickel alloys.
- Generally, it is placed between the boiler radiant part and convection part.
- There are three kinds of superheaters, used in the boilers
– Convection superheater
– radiant superheater
– Conv-radiant superheater.
Economizer
In the furnace, due to the combustion of fuel, flue gas is produced. Economizer is used to recovering some amount of heat energy into the water.
- It works as a heat exchanger.
- It reduces energy losses & increases boiler efficiency.
- It is placed on the flue gas path before the air heater.
Preheater
Air is supplied to the furnace for combustion. Hence, it is most preferable if it is pre-heated before suppling to the furnace.
- Pre-heater is used to pre-heat the air.
- It recovers the heat energy from the flue gas.
- Increase boiler efficiency.
- It dries the pulverizer or the mill.
LP & HP Heater
LP means Low Pressure and HP means High-Pressure heater. To increase the efficiency of the boiler as well as a thermal power plant, condensate water received from the condenser is heated.
- These all are basically heat exchangers.
- In the case of LP heater, water is heated by L.P turbine extracted steam
- In the case of HP heater, water is heated by H.P and I.P turbine extracted steam
- Water is heated before entering the boiler and increase the overall performance.
03. Turbine
The turbine is one of the main parts of the thermal power plant. High-pressure steam from the boiler is passing through the turbine. Due to the high pressure, it exerts a force on the turbine blades and the turbine rotates.

- Steam from the boiler passes through the turbine by a steam pipe.
- Steam at the outlet of the boiler is having high pressure.
- It exerts forces on the vanes of the turbine blades.
- The turbine blades rotate.
- Turbine speed increases drastically based on high pressure.
- The heat energy of the steam is converted into mechanical energy, as it rotates the turbine.
- The turbine produces work as the steam expands in it.
- The turbine has three parts, HP, IP & LP.
- The shaft of the turbine is connected to a generator.
04. Condenser
A condenser means a heat exchanger, it is used to exchange heat between the turbine exhaust and the cooling water. Exhaust from the turbine is cooled in the exchanger and cooling water takes the heat. It has water many tubes and heat exchange happens based on the types of cooling towers.
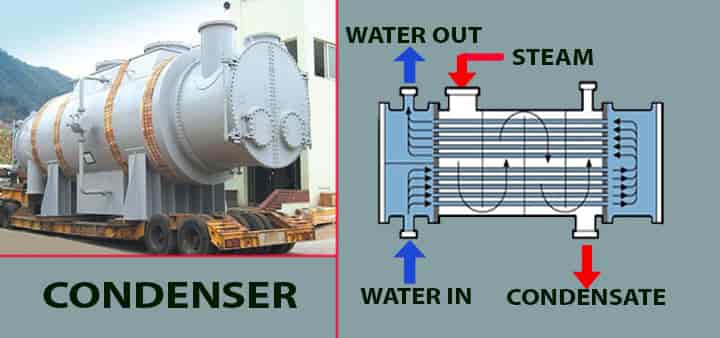
- The turbine exhaust that is the steam, comes below its boiling temperature in the condenser.
- Due to low boiling temperature, steam changed its phase into water.
- The vacuum is created inside the condenser, during this phase change.
- Due to vacuum, steam changes into the water very rapidly.
- The water which is collected at the bottom of the cooling tower is called condensate.
- This condensate is transferred to the boiler through pumps.
05. Condensate Extraction Pumps
This pump helps the supply of condensate from the condenser basin to the deaerator.
06. Deaerator
Before supplying the water from the condenser to the boiler, it is very much necessary to remove all the impurities from the water.
- It removes all dissolved gasses, oxygen, etc.
- No corrosive gases in the feed water
- No corrosion.
07. Boiler Feed Pumps
The boiler feed pump is used to supply water from the deaerator to the boiler drum. It is having a high head to feed the water up to the boiler drum.
08. Cooling Tower
The circulating water picks up the heat from the turbine exhaust and becomes heated. Hence, this heated cooling water needs to be cool to complete the cycle.
This water is cooled in the cooling tower through circulating pumps.
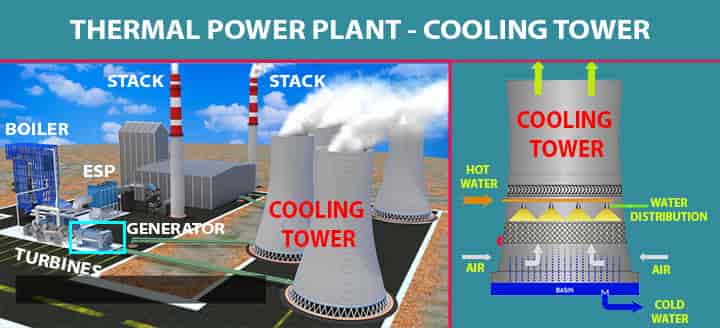
- Heat in the circulating water is rejected in the cooling tower.
- There will be around 2%evaporation loss happens in the cooling tower.
- There are circulating pumps are used to transfer the water in a closed cycle, from the condenser to the cooling tower.
09. Circulating Water (CW) Pumps
These pumps are transferring water from the cooling tower to the condenser.
10. Generator
The generator has a magnetic field, it has a starter, and a rotor. When the steam turbine rotates the generator shaft, it creates a magnetic field and produces electricity.
11. FD Fan & ID Fans
For burning in the combustion of the furnace, fuel is injected. However, the air is required for burning. The fan is pushed the supply air into the combustion chamber of the boiler and continues the entire combustion process. This fan is called a Forced Draft fan or shortly FD fan.
After combustion, flue gas is produced and the same needs to be taken out of the boiler. This is done by another fan, called ID fan or induced draft fan. Apart from these, there are other kinds of fans, used in the system, like,
- PA fan or Primary air fans,
- SA Fan or Secondary air fans
- Gas recirculation fans.
12. Electrostatic Precipitator (ESP)
An electrostatic precipitator (ESP) is another very important to filtrate the air. Due to the combustion of fuel, flue gas consists of ash particles, dust, smoke, foreign particles, etc. which needs to be removed to reduce the air pollution.
It creates a strong electric field to remove all unwanted particles from the flue gas.
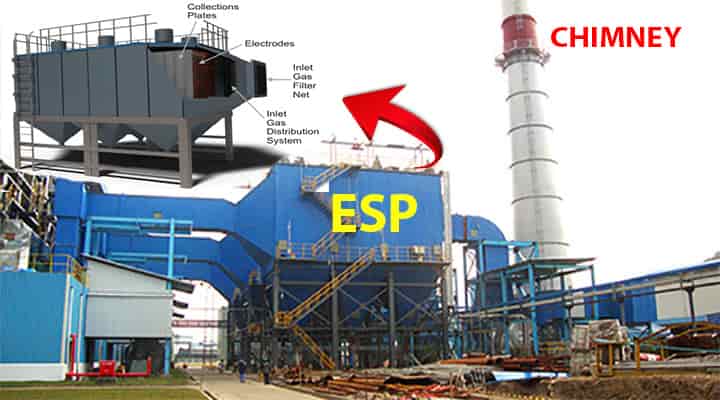

13. Chimney
After ESP, or after the removal of all foreign particles, these flue gases are released to the atmosphere through a chimney.
14. Ash Handling Plant
Each thermal power plant has an ash handling plant. Once the coal is burned, ash is produced, hence, a separate plant is dedicated for the ash handling system.
15. Water supply from a river or canal
A thermal power plant is required for different circuits, like
- Boiler water circuits
- Condensate water circuits
- Cooling water circuits.
For all the circuits, a large quantity of water is required and a continuous water source is required. River or canal water is used for the power plant.
How Does Thermal Power Plant Work? Working Principle
Basic Principle of Thermal Power Plant
The steam turbine is the heart of the thermodynamic cycle, called the Rankine cycle. We have already learned that the Rankine cycle consists of main four components,
- Pump
- Boiler
- Turbine
- Condenser
In the thermal power plant, the working fluid is water which undergoes phase changes.
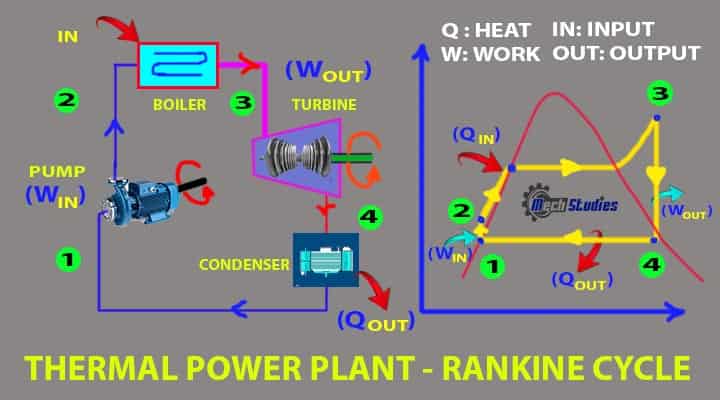
Rankine cycle goes under the following process
Process-1: Isentropic compression (Point 1-2)
- This process incurs the pumping of water.
- Pump absorbs energy, that is basically a work input.
- Water is transferred to boiler which is normally kept at high level, hence, high head of pump with high work input is required.
- High pressure is developed in the water.
Process-2: Heat Addition in boiler at Constant Pressure (Point 2-3)
- High pressure water enters into the boiler and heated through the furnace at constant pressure.
- Due to heating, water is changed it’s phase from liquid to steam.
- Dry saturated vapor is formed.
- This is basically a heat input.
Process-3: Isentropic expansion (Point 3-4)
- In this process, expansion happens in the turbine as dry saturated steam enters & hits the blades.
- This process basically for power output.
Process-4: Heat rejection at constant pressure from the condenser (Point 4-5)
- In this process, wet steam or wet vapor enters to condenser from turbine.
- Heat rejection happens in this stage at constant pressure.
- Steam is changed into saturated water.
Scheme Diagram of Thermal Power Plant
- Steam strikes turbine blades, lose its high pressure and blades rotate.
- Exhaust steam condenses in the condenser.
- This condensed water is supplied to a LP heater i.e. low-pressure heater as well as HP heater i.e. high pressure to increase the temperature of this feed water.
- The turbine is connected to the generator, power is generated.
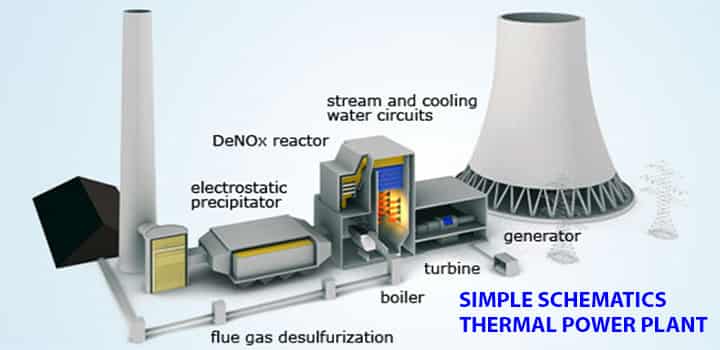
Thermal Power Plant Working Diagram & Principle
The entire working principle is divided into a few parts for better understanding,
Coal Handling System
- Coal is the fuel that is burnt to get thermal energy. Each thermal power plant has it’s own coal handling and ash handling plant.
- Coal is collected from the wagon tippler and fed it to the crusher house through a conveyer belt.
- Crusher house is having a vibrating screen.
- It crushes the coal and makes it granular.
- There may be a primary and secondary crusher house.
- These crusher houses make the coal into a fine powder
- Coarser coals are separated.
- The fine powder is fed to the boiler hopper through a conveyor belt and finally, it is fed to the furnace of the boiler.
Ash Handling System
- After fuel combustion in the furnace, ash is collected through the bottom hopper.
- Fly ash is collected at the bottom of the ESP hoppers.
Boiler Combustion
- Fuel is injected into the boiler.
- Spark is created and combustion starts.
- FD fan is used to supply air into the furnace.
- ID fan is used to release the flue gas from the boiler to the atmosphere through the chimney.
Boiler Water Circuit
- The boiler has water tubes all around the furnace.
- There will be two drums in the boiler, one is at the top i.e. boiler drum and another one is at the bottom, i.e. mud drum
- Both drums are connected to water tubes, a combination of riser and downcomers.
- Water-tube is heated by the furnace, hence, water is also heated.
- Hot water rises up to the boiler drum.
- Coldwater is coming down to the furnace wall and continue the circulation process.
- Gradually the water in the boiler drum becomes hot water and starts to form steam.
- The steam becomes saturated and it again passes through the superheater to make superheated steam.
- Economizer, preheater, reheater are used to increase the efficiency of the boiler.
- This superheated steam is fed to the turbine.
Turbine Circuit
- Superheated steam is high-pressure steam and when it fed to the turbine, it strikes on the turbine blades.
- Pressure energy is changed into mechanical energy.
- Blades start rorating.
- There are H.P, I.P & L.P Turbines, and steam is provided H.P Turbine first.
- The turbine rotates with high speed.
- Turbine exhaust is supplied to the condenser.
Condenser Circuit
- In the condenser, exhaust steam from the turbine is cooled.
- It is basically a heat exchanger.
- This cooling is by a separate cooling water circuit, which is connected to cooling towers.
- Steam comes below its boiling temperature.
- Phase change happens, that is from steam to liquid.
- Basically, condensate forms at the bottom of the condenser.
- Condensate from the condenser is supplied to the boiler through a deaerator.
- This circulation is done by condensate circulation pumps.
- Water is purified in the deaerator, purified means dissolved gasses are removed.
- This water then fed to the boiler through boiler feed pumps.
Cooling Tower Circuit
- The condenser is cooled by a cooling tower.
- Hot water from the condenser is circulated to the cooling towers.
- Cooled in the cooling towers, with the heat exchange between air and water by means of fans.
- Cooled water comes back to the condenser.
- Take the heat from the turbine exhaust and become heated.
- Continues the circuits.
- Water circulation happens by CW (Circulating Water) Pumps.
Generator Circuit
- When the turbine rotates, the shaft also rotates.
- This shaft is connected to a generator.
- The generator is having a starter along with the shaft or rotor.
- Due to the rotation of the rotor high magnetic field is created in the generator.
- Electricity is produced.
- It is stored in the powerhouse through the grid.
Water Treatment Plant
- In a thermal power plant, huge water is required in all the water circuits, at the beginning.
- Later on, due to water losses, in the various system like cooling towers, other losses, make-up water is required.
- This water is treated and demineralized water.
- There are several steps to produce this water which is used to feed as make-up.
- Water treatment consists of a raw water treatment plant, clarifiers, pretreatment plant, RO plant, storage tanks, etc.
Advantages of Thermal Power Plant
There are many advantages of thermal power plants over other kinds of power plants.
- Fuel is coal and it is cheap.
- The power cost is cheap.
- Low installation cost in comparison to other power plants.
- Easy maintenance.
- If fuel is available along with water supply, thermal power plants can opt anywhere.
- Less space with respect to hydropower plants.
- The generation of power is not dependent on nature’s change.
- The commissioning time of the thermal power plant is less comparative to hydro-plants.
- It can run on part load, even at 25% loads.
Disadvantages of Thermal Power Plant
There are few disadvantages of thermal power plants,
- Air pollution
- Global warming
- Running cost is more if we compare with hydro-plants.
- A large water quantity is required.
- The operating cost is high.
- The efficiency of the thermal power plant is less, around 30-35%.
Application of Thermal Power Plant
A thermal power plant produces electricity and that electricity is used in many industries, residential, and all other cases. In a survey, it is shown that around 66% of electricity is produced by thermal power plants in India.
Thermal Power Plant Examples
There are so many thermal power plants in the world, few of them are named below along with their total capacity,
- Taichung Power Plant, Taiwan, 5,788MW
- Shoaiba Power Plant, Saudi Arabia, 5,600MW
- Surgut-2 Power Station, Russia, 5,597.1MW
- Tuoketuo Power Station, China, 5400 MW
- Belchatów Power Station, Poland, 5,354MW
- Kashima Power Station, Japan, 5,204MW
- Vindhyachal Thermal Power Station, Madhya Pradesh, 4,760MW
- Mundra Thermal Power Station, Gujarat, 4,620MW
- Mundra Ultra Mega Power Plant, Gujarat, 4,000MW
- Farakka Super Thermal Power Station, West Bengal, 2,100
Manufacturer of Thermal Power Plant
There are so many manufacturers available in thermal power plants, for example,
- Tata Power,
- JSW Energy
- BHEL
- Toshiba
- Adani Power
- Mitsubishi Power etc.
Overview of Thermal Power Plant
The efficiency of Thermal Power Station or Plant
The overall efficiency of the steam power plant is defined as the ratio of heat equivalent of electrical output to the heat of combustion of coal. The overall efficiency of a thermal power station or plant varies from 20% to 26% and it depends upon plant capacity.
| Installed plant capacity | Average overall thermal efficiency |
| up to 1MW | 4% |
| 1MW to 10MW | 12% |
| 10MW to 50MW | 16% |
| 50MW to 100MW | 24% |
| above 100MW | 27% |
Thermal Power Plant Consideration
Before thermal power plant construction, the following points need to be considered,
- Availability of space.
- Plane land is required.
- Space for future requirements.
- The availability of fuel is coal.
- Availability of water.
- Soil strength should be good enough to hold big foundations.
- Distance from the locality should be sufficient, to avert pollutions.
Thermal Power Plant Efficiency
Efficiency, n = Amount of power generation / (total coal consumtion x cv value of coal)
- n =250 kw/165t/hr x x3500kcal/kg
- n =250000 kJ/sec / 165 x1000kg /3600 x 3500 kcal/kg
- n = 0.3728
- n =37.28%
Conclusion
Hence, we have learned basics of the thermal power plant, along with it’s working principle, parts, etc. Any doubt please don’t forget to write.
Our Videos
Our YouTube Animated Videos
Check a NICE VIDEO
from Learn Engineering for Thermal Power Plant
