What is rivet? or What is riveting process? Any idea! In this article, we will learn the basic rivet definition, meaning, different types, applications, advantages, disadvantages, etc. of riveting system. Let’s explore riveting process!
What is a Rivet? Riveting Process, Definition, Meaning
Let’s learn about the basics of rivet as well as riveting process.
What is a Rivet?
The rivet is one of the popular and known mechanical fasteners. You have seen this everywhere in the use from your little toys to electronic parts.
- The rivets are easy, replaceable fasteners.
- It has a head and a tail; the tail is cylindrical parts and the heat has semi-circular with a little bit down-sized structure.
- Obviously, you know how the rivets look like, but still read it.

Rivet Definition or Riveting Definition
A short metal pin or bolt for holding together two plates of metal, its headless end being beaten out or pressed down when in place.
Rivet Meaning
Rivets are like non-threaded fasteners that are usually manufactured using steel or aluminium.
- When the rivet is going to be installed the rivet is placed in a punched or drilled hole and the tail kind of upset so that it will expand to about 1.5 times the original shaft diameter.
- The pounding and pulling will create a head on the other end and the tail end will be a flatter one.
- So, the final shape will be like a dumbbell-shaped.
- You may have known about the rivets all along but did you know it’s the names of parts. It easy, one is rivet head, rivet pin, and the end its rivet end. Let’s know a brief about the process of riveting now.
Riveting Process
We know now the rivet parts like rivet head, rivet pin and the rivet end. These are the basic parts of the rivet and they are easy to recognize. Coming to the riveting, it is the forging process that may be used power for fixing the parts together by engrossing and facilitating the use of metal part known as the rivet.
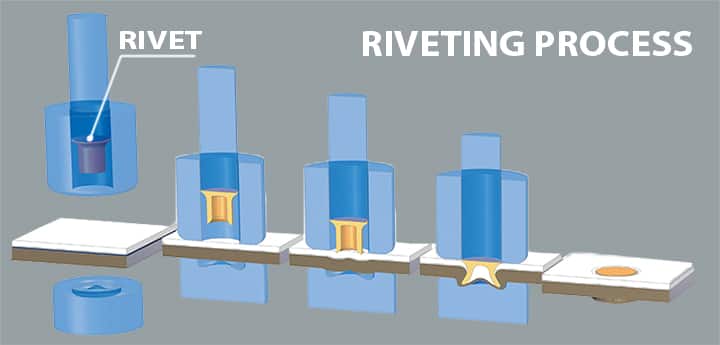
- Just in simple words the parts used to join together with the help of the rivet is known as the riveting process.
- The rivets are kind of the adjacent surfaces between the two parts to be joined.
- A straight metal piece will be inserted via the hole or cavity provided for the two materials to be joined.
- It will form a connection and thus the parts will be joined securely.
- The riveting process can be done for the hollow as well as the solid workpieces.
How Do Rivet Work? Riveting Process Working Process
We have already learned the definition of rivet, now, let’s see how do rivet work? The rivets can be used by incorporating different methods. The installed rivet is either drilled, place or punched into a hole, the tail is deformed and thus holding the rivet in place.
- The rivet is generally deformed by pounding or smashing of the tail that will make the material flatter causing to increase in the diameter.
- When pounding is finished the tail has the appearance of the dumbbell shape completing the rivet joint. You can read our another article: Soldering Process
How the Riveting is done?
This is a usual process you may have known already. But still, for the sake of understanding let’s check it out now.
- Firstly, the hole drilled or punched in the place or parts that need to riveted using the rivet.
- Though punching of the hole might be easy for the thin plates but it’s difficult in case of the thick plates and parts.
- Different types of pressurized methods are employed for punching the holes in those parts.
- Though in large pressure vessels punching is not suited, drilling of the hole is used preferably.
Check a NICE VIDEO from ACE Hardware,
Coming back, the rivet hole is about 1.5 mm times larger than the diameter of the rivet. We will need to remove the burs and chips for getting the tight plate joint. The rivet will be placed in the hole, the tail deformed and the tail portion expands about 1.5 times of its shank diameter.
- The riveting can be done manually for small applications, for other applications using machines like a pneumatic hammer
 the riveting is done.
the riveting is done. - For our usual hand riveting, a big blow using the hammer is simply to provide thrust on the rivet.
So, what are the material requirements of rivets, what properties should the material of the rivet have? Let’s check them out now.
- ▲【VARIOUS MANDRELS】The rivet nut toolquipped with 7PCS interchangeable mandrels(Metric M6 M8 M10; SAE 1/4-20*2, 5/16-18, 3/8-16).
- ▲【EASY FOR USE】The mandrel of Wetols 14" Rivet Nut can be easily removed by hand for easy mandrel change or maintenance.
- ▲【STURDY AND DURABLE】The mandrels of our hand rivet nut tool is made from Chrome steel with heat treated 40℃ and the arm is made from 45 carbon steel, which protect against corrosion and resist to deformation.
- ▲【SOLID BLOW CASE】All Accessories are packaged in the blow molded carry case for easy storage and portability. Each tool is placed close to its position to prevent movement and scratching.
- ▲【COMPLETE ACCESSORIES】70pcs rivet nuts (10 rivet nuts for each mandrel,20 rivet for SAE 1/4-20).Please note that the 1/4-20 mandrel was installed in the gun.
Materials Used for Rivets
The material used for the rivets should have ductility and toughness. They are usually made of,
- steel low carbon steel or
- carbon steel,
- brass,
- aluminium or
- copper.
When the requirement is of a fluid-tight joint then the steel rivets are used. Now let’s check out the different types of rivets.
Types of Rivets
The rivet can be various types , as follows,
, as follows,
- Blind rivets
- Solid rivets
- Drive rivets
- Semi tubular
- Split type
- Threaded rivets
- Oscar rivets
- Flush rivets
- Friction lock rivets
- Self-piercing rivets, etc.
Description of Rivet Types & Along with Each Riveting Definition
Blind Rivets
As the name suggests they can be completely installed from one side. They are ideal for projects in which the access to the joint is limited to only one side.

These are available in standard, structural, closed-end, and other various styles and for a wide range of applications.
- Blind rivets are also commonly referred as the pop rivets.
- These are tubular with the nail-like mandrel through the centre that has necked area near the head.
- The rivet assembly is inserted into a hole drilled through the parts to be joined and a specially designed tool is used to draw the mandrel through the rivet.
Solid Rivets
The solid rivets are the simplest to use, strong, reliable, and oldest type of fasteners.

- It has the solid shaft with head on one end when they are installed once the headless end of the solid rivet is deformed with hammer or rivet gun to hold it in place.
- These rivets have long history with archaeological findings of bronze age.
A rivet compression or crimping tool can also deform this type of rivets. This tool is mainly used on rivets close to the edge of the fastened material since the tool is limited by the depth of its frame.
Drive Rivets
The drive rivets have a short mandrel that protrudes from the head. Once the drive rivet is inserted into a hole the mandrel is driven in with the help of a hammer to flare out the end of the rivet that is inside the hole.

- The drive rivet us generally used for the rivet wood panel, since the hole is not need to be drilled all the way through in case of wood panel.
- It produces a well aesthetic experience.
Semi Tubular Rivets
Semi tubular rivets are similar to solid rivets but contain a hole at the end of the rivet opposite the head. This hole causes the tubular portion of the rivet (around the hole) to roll outward when force is applied.

- Semi tubular rivets also require less force needed for application and assembly.
- The installation tools for these are the handset, manual squeezer, pneumatic squeezer, kick press, impact riveter, and PLC controlled robotics.
- The common use of the semi-tubular rivets is in the brakes, ladders, binders, HVAC ductwork etc.
Split Rivets
The one ideal for piercing through softer materials like woods, leather, and plastic are the split rivets. Split rivets are also the standard home repair rivets.

- The structure is like sawed or split bodies having sharp ends to make their own hole through the leather, fibre plastic or soft metals.
- The split rivets are not used generally in critical applications.
Threaded Rivets
Threaded inserts and rivet nuts provide a uniquely strong permanent thread through sheet materials and other materials where installation is only possible from one side.

- Threaded Rivets has a threaded internal mandrel (stem) with the external portion machined flat on two sides for the tool to grip and rotate.
- The head is normally hexagonal to prevent rotation of the tubular body while the mandrel is being torqued and broken off.
Oscar Rivets
Don’t go onto the name it not like an award. The Oscar rivets are kind of similar to the blind rivets just like sometimes the Oscar awards are given blindly.

Anyway, Oscar rivets are blind in appearance with split like along the hollow shaft.
- These splits cause the shaft to fold and flare out as the mandrel is drawn into the rivet.
- This flare provides a wide bearing surface that reduces the chance of rivet pull-out.
- This design is ideal for high vibration applications where the back surface is inaccessible.
Flush Rivets
The flush rivet is commonly used in external metal surfaces where the good appearance and the elimination of unnecessary aerodynamic drag are important.

- Also, the flush rivets take the advantage of countersunk rivet hence the reason flush rivets are also known as the counter sunk rivets.
- These are used mostly on the exterior of aircraft for aerodynamic reasons.
Friction Lock Rivets
One early form of the blind rivets that was the first to be widely used for aircraft construction and repair was the Cherry friction-lock rivets.

- Originally, Cherry friction-locks were available in two styles, hollow shank pull-through, and self-plugging types.
- The pull-through type is no longer common; however, the self-plugging Cherry friction-lock rivet is still used for repairing light aircraft.
Self Piercing Rivets
The last type of rivet is the self-piercing rivets. If you don’t know the self-piercing, it is simply the process of joining two or more materials using engineered rivets.

- The rivets like blind, semi-tubular require drilled or punched hole, self-piercing ones doesn’t require drilled or punched hole.
- Self-piercing rivets are cold-forged to a semi-tubular shape and contain a partial hole to the opposite end of the head.
So, that was a long list of the type of rivets. Now let’s see the advantages and disadvantages of the rivets as well as riveting process and their applications.
Advantages of Riveting Process
The advantages of riveting are as follows,
- The process of riveting is an inexpensive method. One of the reasons is the production of cheap.
- There is no compulsion of ferrous or non-ferrous materials both the metals can be joined with the process of riveting.
- Apart from metals it can also be used for the non-metals like wood, plastic, asbestos sheet etc.
- Like in welding similar metals are joined, but there are no requirements of the similar materials, you can join even the dissimilar materials.
- No fumes, gases are produced in riveting unlike welding, the process or riveting is environment friendly.
- They have high shear strength and good fatigue resistance.
- The riveted joints can be made without the constraints of location.
Disadvantages of Riveting
The disadvantages of riveting are as follows,
- The process of riveting takes more labour time than the welding.
- Additional operations like the layout and drilling, holes are necessary hence the labour cost of rivets joints is also high.
- The holes may weaken the working cross-section of the plate. Then the additional thickness is required to compensate for this problem. This additional thickness and overlapping of plates for riveting increase metal consumption.
- Stress concentration at the rivet holes of metal plates.
Applications of Riveting Process
The application of the riveting process is wide, as follows,
- Fastening of the sheets and rolled shaped metals.
- For the aircraft structure where the aluminium metal is used.
- Riveted joints are used where the metals have poor weldability.
- They are used in lap, abutment, and double-cover plate joints.
- The high strength rivets are used in constructing the metal bridge, hoisting cranes, boiler and pressure tanks.
Conclusion
Hence, we got a basic idea about the rivet as well as the riveting process. In addition, we have also learned rivet definition, meaning, and various types of rivets. Do you have any questions on the riveting definition?


I am not sure where you’re getting your information, but good topic. I needs to spend some time learning more or understanding more.
Thanks for great information I was looking for this information for my mission.
Thanks for magnificent info I was looking for this info for my mission.
I am now not certain the place you’re getting your info, but good topic. I needs to spend some time learning much more or figuring out more. Thanks for excellent info I was searching for this info for my mission.